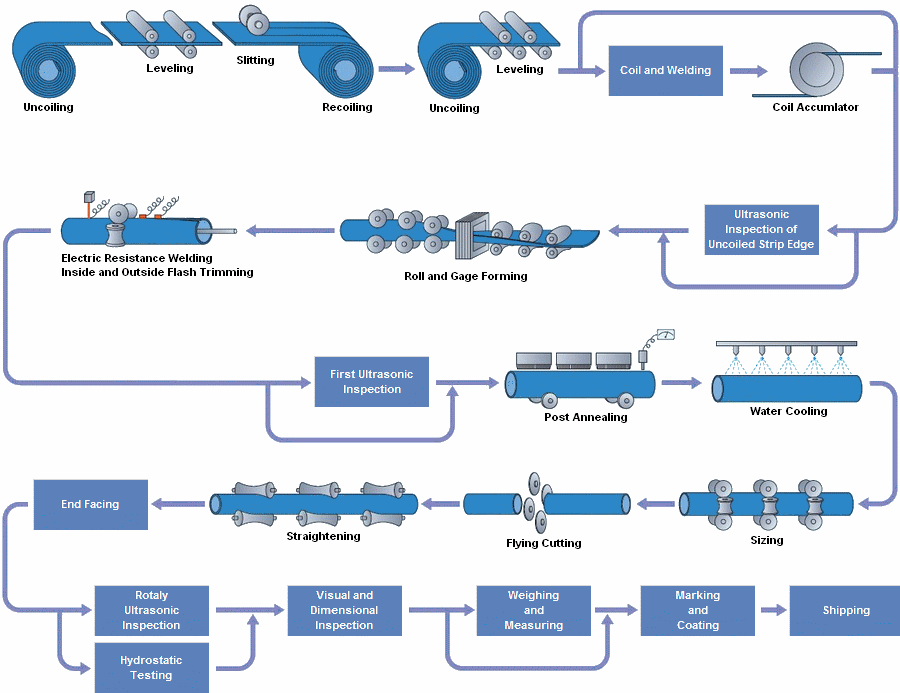
Highlights of the Longitudinally Welded Pipes
Specification
• ASME 36.10, ASME 36.19 are the key specifications covering the standardization of dimensions of welded and seamless wrought steel pipe. ASME B16.25 covers the preparation of butt weld connections between pipes and ASME B16.49 covers the marking details.
• Specifications for API 5L adhere to the International Organization for Standardization ISO 3183, standardizing pipeline transportation systems within the materials, equipment and offshore structures for natural gas, petroleum, and petrochemical industries. When authoring the standards, the technical committee recognized that there are two basic Product Specifications Levels (PSL) of technical requirements and therefore developed PSL-1 and PSL-2. PSL-1 is a standard quality for line pipe where PSL-2 contains additional chemical, mechanical properties, and testing requirements.
• PSL-1 is a loose standard quality for line pipe, whereas PSL-2 contains additional testing requirement, stricter chemical physicals, along with different ceiling limits of mechanical properties, and require Charpy impact testing conditions.
Length of Pipes
• Piping lengths from the factory not exactly cut to length but are normally delivered as:
○ Single random length has a length of around 5-7 meter
○ Double random length has a length of around 11-13 meter
Shorter and longer lengths are available, but for a calculation, it is wise, to use this standard lengths; other sizes are probably more expensive.
Other Properties
• The manufacturing of Double Submerged Arc Welded Pipe involves first forming steel plates into cylindrical shapes. Then the edges of the rolled plate are formed so that V-shaped grooves are formed on the interior and exterior surfaces at the location of the seam.
• For the ends of pipes are 3 standard versions available.
○ Plain Ends (PE)
○ Threaded Ends (TE)
○ Beveled Ends (BE)
The PE pipes will generally be used for the smaller diameters pipe systems and in combination with Slip On flanges and Socket Weld fittings and flanges.
The TE implementation speaks for itself, this performance will generally used for small diameters pipe systems, and the connections will be made with threaded flanges and threaded fittings.
The BE implementation is applied to all diameters of buttweld flanges or buttweld fittings, and will be directly welded (with a small gap 3-4 mm) to each other or to the pipe. Ends are mostly be beveled to angle 30° (+ 5° / -0°) with a root face of 1.6 mm (± 0.8 mm).
Materials
Carbon Steel & Alloy Steel:
SA53 / A53 Welded -Grade B,
API 5L Welded -Grades (B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70 and X80) PSL 1, PSL 2
Low Temperature Carbon Steel:
A333 / A333M (Gr. 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11),
ASTM A334 / A334M
Stainless Steel:
ASTM A312 TP(304, 304H, 304L, 309, 310, 316, 316L, 317L, 321, 347)
ASTM A409 TP(304, 304L, 309, 310, 316, 316L, 317L, 321, 347)
ASTM B673 (UNS N08925, UNS N08354, and UNS N08926)
Duplex / Super Duplex Steel: ASTM A790 (UNS S31803, S32205, S31500, S32550, S31200, S31260, S32304, S39274, S32750, S32760, S32900, S32950, S39277, S32520, S32906, S32003)
Nickel Alloy:
ASTM B514, ASTM B517 (UNS N06600, UNS N06603, UNS N06025, and UNS N06045), ASTM B619 / B619M, ASTM B705 (UNS N06625, N06219 and N08825), ASTM B725 (UNS N02200/UNS N02201, UNS N04400), ASTM B775 / B775M, ASTM B464 / B464M (UNS N08020)
Standard
ASME 36.10, ASME 36.19 are the key specifications covering the standardization of dimensions of welded and seamless wrought steel pipe. ASME B16.25 covers the preparation of butt weld connections between pipes and ASME B16.49 covers the marking details.
ASME 36.10
This standard covers the standardization of dimensions of welded and seamless wrought steel pipe for high or low temperatures and pressures. Pipe NPS 12 (DN 300) and smaller have outside diameters numerically larger than corresponding sizes. In contrast, the outside diameters of tubes are numerically identical to the size number for all sizes.
The size of all pipe is identified by the nominal pipe size. The manufacture of pipe NPS ⅛ (DN 6) to NPS 12 (DN 300), inclusive, is based on a standardized outside diameter (O.D.). This O.D. was originally selected so that pipe with a standard O.D. and having a wall thickness that was typical of the period would have an inside diameter (I.D.) approximately equal to the nominal size. Although there is no such relation between the existing standard thickness – O.D. and nominal size – these nominal sizes and standard O.D.s continue in use as “standard.” The manufacture of pipe NPS 14 (DN 350) and larger proceeds on the basis of an O.D. corresponding to the nominal size.
ASME 36.19
This Standard covers the standardization of dimensions of welded and seamless wrought stainless steel pipe for high or low temperatures and pressures.
Pipes NPS 12 (DN 300) and smaller have outside diameters numerically larger than their corresponding sizes. In contrast, the outside diameters of tubes are numerically identical to the size number for all sizes. The wall thicknesses for NPS 14 through 22, inclusive (DN 350-550, inclusive), of Schedule 10S; NPS 12 (DN 300) of Schedule 40S; and NPS 10 and 12 (DN 250 and 300) of Schedule 80S are not the same as those of ASME B36.10M. The suffix S in the schedule number is used to differentiate B36.19M pipe from B36.10M pipe. ASME B36.10M includes other pipe thicknesses that are also commercially available with stainless steel material.
API 5L
ANSI / API 5L specifies the manufacture of two product levels (PSL1 and PSL2) of seamless and welded steel pipe for the use of a pipeline in the transportation of petroleum and natural gas. For material use in a sour service application, refer to Annex H; for offshore service application, refer to Annex J of API 5L 45th Edition.
Grades covered by this specification are A25, A, B and “X” Grades X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70, and X80. The two digit number following the “X” indicates the Minimum Yield Strength (in 000’s psi) of pipe produced to this grade.
Application of longitudinal welded pipe